A properly-fit respirator is designed to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne contaminants such as dusts, fumes, vapors, and infectious agents associated with inhaling small and large particle droplets.
Without adequate respiratory protection, employees may be at risk of developing health conditions like lung diseases, cancer, or other respiratory illnesses.
Respiratory Protection – No. 3 in the Top 10 most frequently penalized OSHA standards for 2022.
29 CFR 1910.134 is an OSHA standard that provides requirements for establishing and maintaining a respiratory protection program.
It applies to all occupational situations where respirators are necessary to protect the health of the worker or where the employer requires respirator use.
If employees are required to use a respirator, the employer is required to:
Train employees on the proper use of the respirators
Create a written respiratory protection program
Select NIOSH approved respirators
Ensure employees are medically approved to wear a respirator
Fit test employees annually using an OSHA-accepted qualitative or quantitative protocol to ensure the respirators fit
There are several types of respirators, each designed for specific purposes and levels of protection.
- Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA): Provide breathable air from a tank, used in environments with toxic gases or where oxygen levels are low, such as firefighting
- Half Mask/Dust Mask: Filter out a specific amount of airborne particles, including large respiratory droplets and smaller aerosol particles.
- Half-Face Respirators (Elastomeric): Cover the nose and mouth, and equipped with replaceable filters for particulates or gases. Typically used in industrial settings.
- Full-Face Respirators (Elastomeric): Cover the entire face and provide a higher level of protection against particulates and harmful gases.
- Powered Air-Purifying Respirators (PAPRs): Use a battery-powered blower to pull air through filters, providing a constant supply of clean air. These can be used with hoods or helmets.
- Supplied Air Respirator (SAR): SARs are used when air-purifying respirators (APRs) are not adequate, such as in environments with unknown chemicals or immediately dangerous to life and health (IDLH).
There are 9 filter types for use with non-powered APRs.
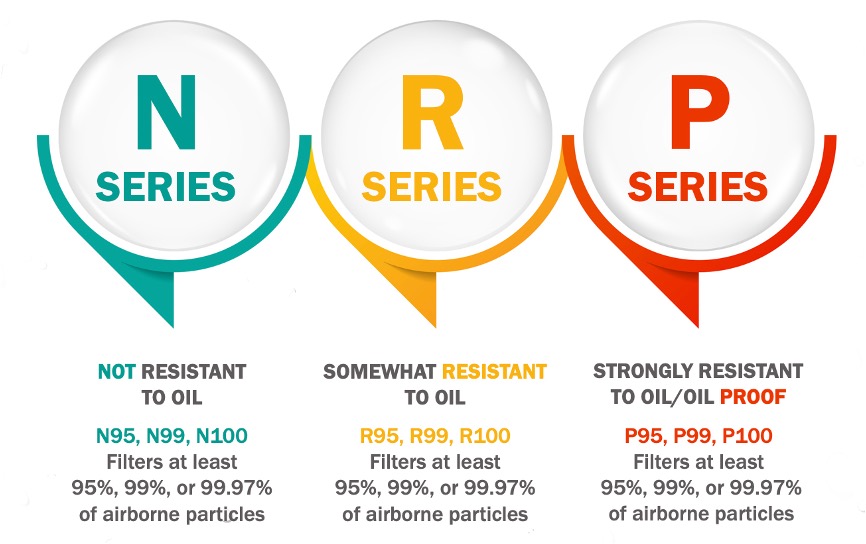
R or P series filters need to be used when the oil component in products may become airborne. (fuel, lubricating or hydraulic oils, solvents, paints, and pesticides)
Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) is the maximum level of a specific airborne hazard that an employee can be exposed to over an 8-hour period.
Assigned Protection Factors (APF) is the workplace level of respiratory protection a respirator will provide.
Maximum Use Concentrations (MUC) is the maximum atmospheric concentration of a hazardous substance.
You must select a respirator that meets or exceeds the required level of employee protection!
